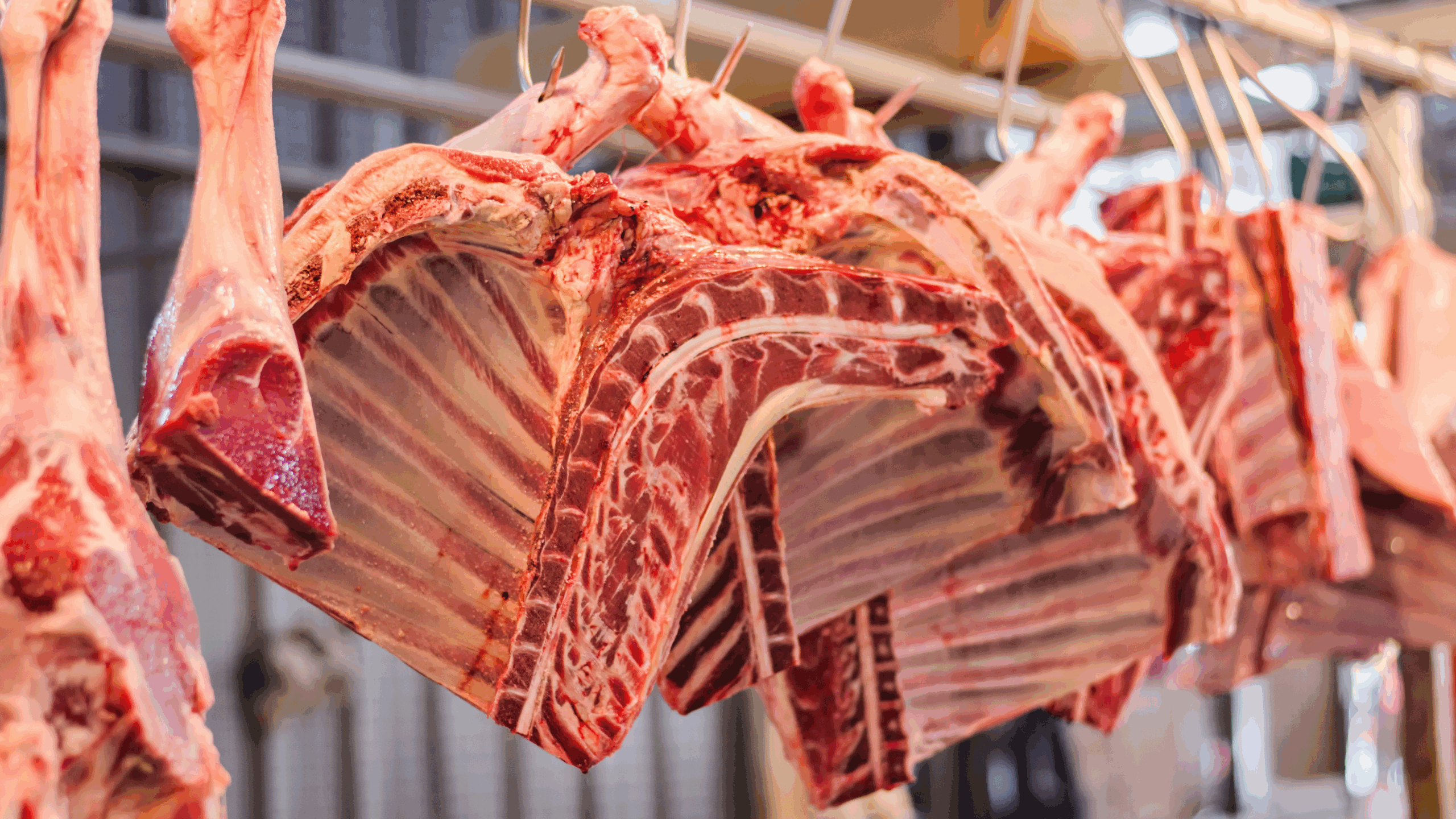
When talking about beef, it is important to understand that meat can be sold at several levels of cutting, which affect the price, convenience, and how the meat is used. The cuts can be divided into three main categories:
Whole Carcass
Primal Cuts / Subprimal Cuts
Retail Cuts / Consumer Cuts
What it is: Purchasing the entire animal or a large portion of it without significant internal division.
Advantages:
Suitable for breeders or restaurants that need large quantities.
Allows flexibility in cutting and producing different cuts.
Disadvantages:
Requires professional knowledge in cutting and preparation.
Storage and transportation require appropriate equipment.
What it is: Dividing the carcass into main cuts (Primal Cuts), such as:
Chuck – shoulder
Rib – ribs
Loin – sirloin/tenderloin
Round – hindquarter
Brisket – chest
Shank – leg
At this stage, it is also possible to divide into Subprimal Cuts, smaller cuts from the main cuts, preparing them for retail cutting.
Advantages:
Allows extraction of higher quality cuts according to demand.
Suitable for restaurants, butcher shops, and wholesale.
Disadvantages:
Still requires knowledge in cutting and maintaining meat quality.
What it is: Cuts ready for sale to individual customers or restaurants. Common examples:
Ribeye / Entrecôte – rib steak
T-bone / Porterhouse – bone-in steak
Sirloin / Striploin – sirloin
Tenderloin – filet
Stew Meat – meat for stew or braising
Advantages:
Convenient for the consumer, ready for immediate use.
Allows maximizing sales according to steak types and popular dishes.
Disadvantages:
Less flexibility in creating unique cuts.
Higher price per unit of meat due to cutting and preparation.
🔹 Summary
The choice of cut type mainly depends on the intended use:
Whole carcass – suitable for breeders, large restaurants, or butcher shops with independent cutting capabilities.
Primal cuts – suitable for restaurants and wholesalers, allows preparation of high-quality cuts according to demand.
Retail cuts – suitable for private customers and direct sale, convenient for immediate use.
Understanding the differences between the cut levels allows everyone working with meat – from butchers to chefs and restaurant owners – to choose the most suitable format, save costs, and maintain meat quality over time.